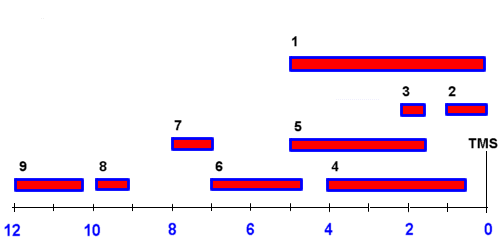
Alternatively, the 9 regions may be selected using the links below:
| Type of proton. | Chemical shift (d ppm) |
|---|---|
| Alkyl, RCH3 | 0.8-1.0 |
| Alkyl, RCH2CH3 | 1.2-1.4 |
| Alkyl, R3CH | 1.4-1.7 |
| Allylic, R2C=CRCH3 | 1.6-1.9 |
| Benzylic, ArCH3 | 2.2-2.5 |
| Alkyl chloride, RCH2Cl | 3.6-3.8 |
| Alkyl bromide, RCH2Br | 3.4-3.6 |
| Alkyl iodide , RCH2I | 3.1-3.3 |
| Ether, ROCH2R | 3.3-3.9 |
| Alcohol, HOCH2R | 3.3-4.0 |
| Ketone, RCOCH3 | 2.1-2.6 |
| Aldehyde, RCOH | 9.5-9.6 |
| Vinylic, R2C=CH2 | 4.6-5.0 |
| Vinylic, R2C=CRH | 5.2-5.7 |
| Aromatic, ArH | 6.0-9.5 |
| Acetylenic, RC=CH | 2.5-3.1 |
| Alcohol hydroxyl, ROH | 0.5-6.0a |
| Carboxylic, RCOOH | 10-13a |
| Phenolic, ArOH | 4.5-7.7a |
| Amino, R-NH2 | 1.0-5.0a |
| Type of carbon atom | Chemical shift (d ppm) |
|---|---|
| Alkyl, RCH3 | 0-40 |
| Alkyl, RCH2R | 10-50 |
| Alkyl, RCHR2 | 15-50 |
| Alkyl halide or amine , (CH3)3C-X (X = Cl, Br, NR2) | 10-65 |
| Alcohol or ether, R3COR | 50-90 |
| Alkyne, -C= | 60-90 |
| Alkene, R2C= | 100-170 |
| Benzylic carbon | 100-170 |
| Nitriles, -C=N | 120-130 |
| Amides, -CNR2 | 150-180 |
| Carboxylic acids, esters, -COOH | 160-185 |
| Aldehydes, ketones, -C=O | 182-215 |
 Return to Chemistry, UWI-Mona,
Home Page
Return to Chemistry, UWI-Mona,
Home Page
Copyright © 2003 by Robert John Lancashire, all rights reserved.
Created and maintained by Prof. Robert J. Lancashire,